Total Knee Replacement Surgery
Categories
Cardiology
————————————————-
Urology
————————————————-
Total knee replacement
————————————————-
Total hip replacement
————————————————-
Laparoscopic surgery
————————————————-
Diagnostic services
————————————————-
General surgery
————————————————-
Arthroscopy
————————————————-
Neurology
————————————————-
Orthopedics
————————————————-
Spine
————————————————-
Diabetology
————————————————
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
A total knee replacement replaces your diseased knee joint with man-made components, eliminating the damaged bearing surfaces that are causing pain. A diagnosis of advanced osteoarthritis of the knee will indicate the need for total replacement of the knee joint.
While you may think of the knee as a hinge, it is really much more complex. The various surface components of the knee roll and glide as the joint bends. The different knee replacement implants on the market try to replicate these motions. iTotal® Patient-Specific Knee Replacement System (ConforMIS) Based upon your age and lifestyle, there are several design options to choose from that will help you return to an active, enjoyable life. Ultimately, your surgeon will make an implant recommendation (both design and brand) based upon his or her skill and experience with a particular device as well as your specific circumstances and needs.
It is, however, important to understand the differences between implants so that you can engage intelligently with your surgeon on the subject.
Implant Components
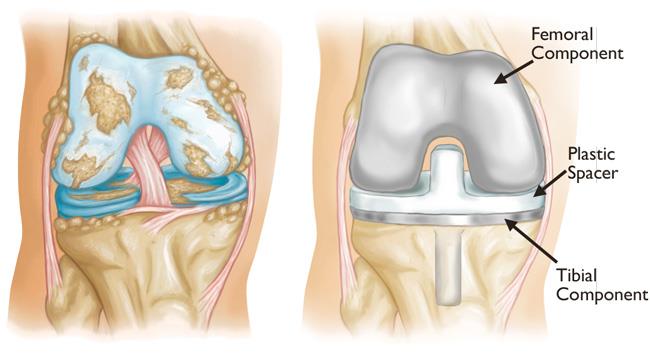
There are three components to a knee implant, replacing three bone surfaces – femoral, tibial and patellar implants. The components weigh between 10 to 15 ounces in total.
Femoral Component
Arthroscopy is a procedure for diagnosing and treating joint problems. During arthroscopy, a surgeon inserts a narrow tube containing a fiber-optic video camera through a small incision — about the size of a buttonhole. The view inside your joint is transmitted to a video monitor. In a knee implant, the femoral component, made of metal, curves up around the end of the femur (or thighbone). It has a central groove allowing the patella (or kneecap) to move up and down smoothly as the knee joint bends and straightens.
Patellar Component
The patellar ‘button’ is a dome-shaped piece of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene that replicates the surface of the kneecap.
Implant Materials
These are designed such that a metal component always moves against plastic or other synthetic material. This promotes smooth movement and minimal future wear. The metal parts of the implant are usually created from titanium or cobalt/chromium-based alloys. The plastic parts are an ultrahigh-molecular weight polyethylene.

